India’s share of high technology exports in its total manufactured exports have continued to remain low. Within the select economies mentioned in the table below, other Asian economies like China and South Korea have the highest share of high technology exports in their manufactured exports. Export orientation can play an important role in the growth of an economy. Forbes (2016) mentions how export promotion in countries like China and South Korea played a key role in increasing competition and improving technical capability of their firms.1
Table 1: High Technology Exports as Share of Manufactured Exports for Select Countries
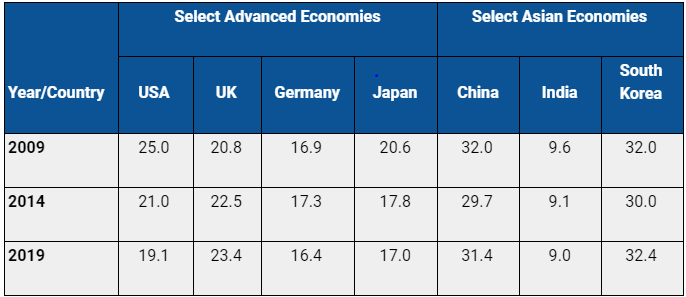
Based on the SITC Rev 4., the high technology sectors include Aerospace, Computers-office machines, Electronics-telecommunications, Pharmacy, Scientific instruments, Electrical machinery, Chemistry, Non-electrical machinery, Armament.2
The table below captures the number of firms from the select sample of countries that make it to the list of the top 2,500 global firms by R&D expenditure3 and are present in these high technology sectors. As can be seen from the table, apart from the Pharmaceuticals & Biotechnology sector, India does not have any presence in any of the other high technology sectors. On the other hand, countries with a large share of high tech exports in their manufactured exports have a presence in almost all of these sectors.
Table 2: Sector-wise Global Industrial R&D Expenditure and Country-wise Number of Firms (2019)
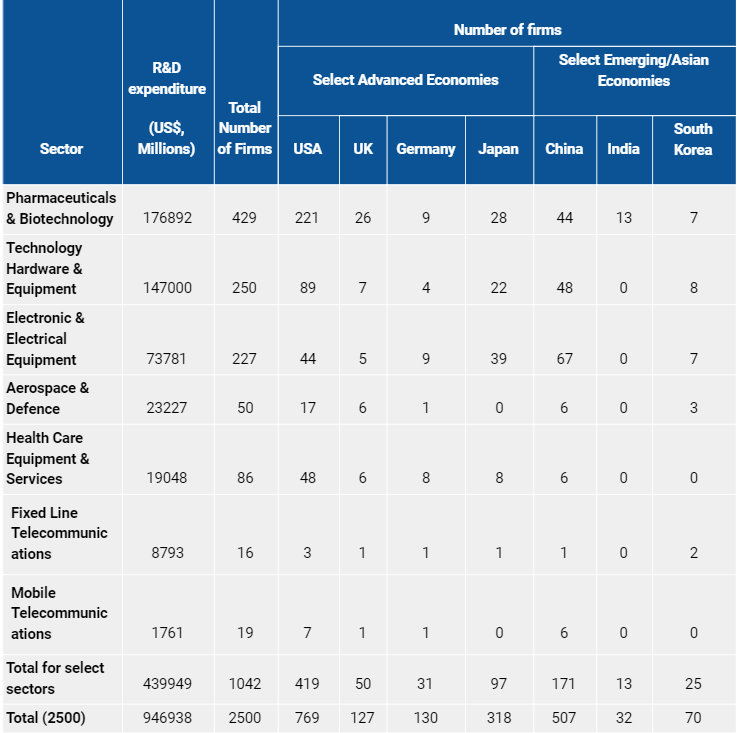
Note: Figures in euros were converted to dollars using the EUR-USD exchange rate of 1.15 as at 31 December 2018 and as mentioned in the EU Industrial R&D Investment Scoreboard
The low share of high-tech exports and the poor presence of Indian firms in the high-tech R&D sectors, can be explained by the low level of spending on R&D undertaken in India. India’s R&D spending as a share of GDP has been stuck in a range of 0.6 to 0.9 percent for the past thirty years, with the government sector dominating the national R&D expenditure with a share of 52 percent.4 Private sector accounted for 41 percent of national R&D spending as of 2017-18.5 Sandu, Steliana and Ciocanel, Bogdan (2014) have shown that private sector investment in R&D has a stronger influence on high-tech exports than investment by the public sector.6 It would be important for Indian industry to invest significantly more on R&D, and become more export oriented to not only enhance its own technical capability but also that of the country.
- Forbes (2016), India’s National Innovation System: Transformed or Half-formed?
- https://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/cache/metadata/Annexes/htec_esms_an5.pdf
- EU Industrial R&D Scoreboard 2019
- CTIER Handbook: Technology and Innovation in India 2019
- Department of Science and Technology (DST), Research and Development Statistics at a Glance 2019-20
- Sandu, Steliana and Ciocanel, Bogdan (2014); Impact of R&D and Innovation on high – tech export